Amoeba sisters video recap incomplete dominance codominance answer key – The Amoeba Sisters Video Recap: Incomplete Dominance and Codominance Answer Key provides a comprehensive overview of these genetic concepts, offering a valuable resource for students and educators alike. This guide delves into the intricacies of incomplete dominance and codominance, shedding light on their genetic mechanisms and phenotypic implications.
Through engaging explanations, illustrative examples, and a thorough analysis of the Amoeba Sisters video, this recap empowers readers to grasp the complexities of these genetic phenomena, fostering a deeper understanding of their significance in shaping phenotypic expression.
Incomplete Dominance
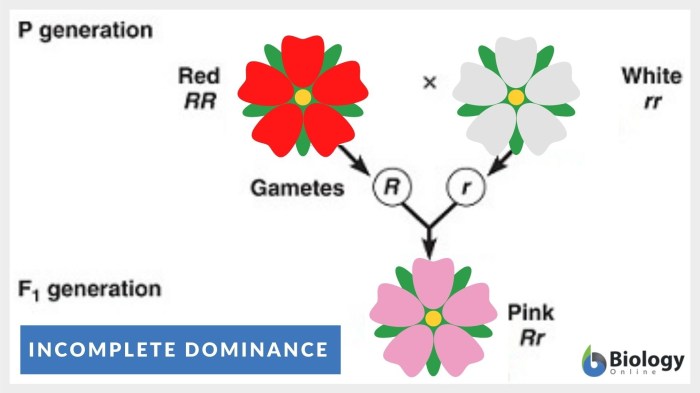
Incomplete dominance is a genetic pattern in which the heterozygous genotype exhibits a phenotype that is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes. This occurs when neither allele is dominant over the other, resulting in a blending of the two traits.
Examples of incomplete dominance include:
- Flower color in snapdragons: When red and white snapdragons are crossed, the offspring have pink flowers.
- Seed coat color in peas: When yellow and green peas are crossed, the offspring have yellow-green seeds.
- Feather color in chickens: When black and white chickens are crossed, the offspring have blue feathers.
The genetic mechanisms underlying incomplete dominance involve the incomplete expression of both alleles in the heterozygous genotype. The dominant allele does not fully mask the expression of the recessive allele, leading to a blended phenotype.
A Punnett square for incomplete dominance can be illustrated as follows:
| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| R | RR (red) | Rr (pink) |
| r | Rr (pink) | rr (white) |
Codominance
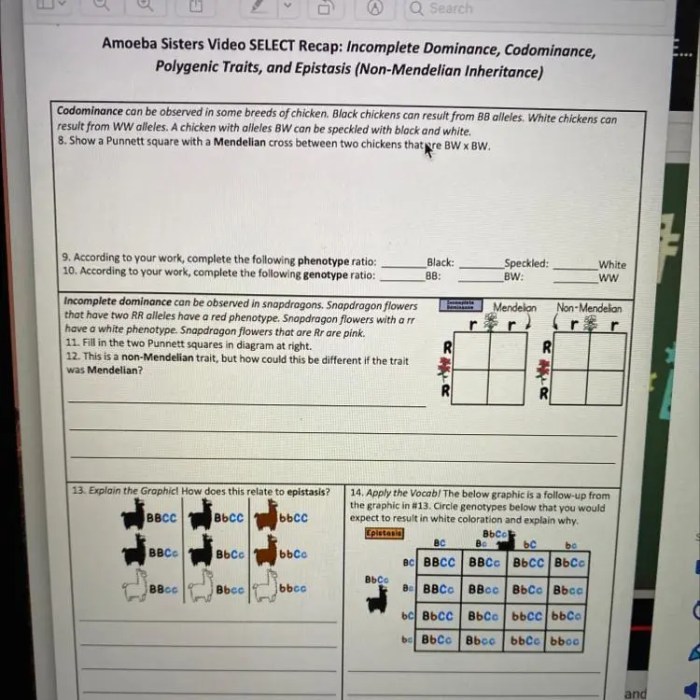
Codominance is a genetic pattern in which both alleles in the heterozygous genotype are fully expressed, resulting in a distinct phenotype that is not intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes.
Examples of codominance include:
- Blood type in humans: The A and B alleles for blood type are codominant, resulting in the AB blood type in heterozygous individuals.
- Flower color in four o’clock plants: The red and white alleles for flower color are codominant, resulting in pink and white striped flowers in heterozygous individuals.
- Feather color in Andalusian chickens: The black and white alleles for feather color are codominant, resulting in a blue-grey speckled pattern in heterozygous individuals.
The genetic mechanisms underlying codominance involve the complete expression of both alleles in the heterozygous genotype. Neither allele is able to mask the expression of the other, leading to a distinct phenotype.
A Punnett square for codominance can be illustrated as follows:
| A | B | |
|---|---|---|
| A | AA (type A) | AB (type AB) |
| B | AB (type AB) | BB (type B) |
Comparison of Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
Incomplete dominance and codominance are both genetic patterns that result in the expression of both alleles in the heterozygous genotype. However, there are key differences between the two patterns:
- Phenotype:In incomplete dominance, the heterozygous genotype exhibits an intermediate phenotype, while in codominance, the heterozygous genotype exhibits a distinct phenotype that is not intermediate.
- Genetic mechanisms:In incomplete dominance, neither allele is fully dominant over the other, while in codominance, both alleles are fully expressed.
- Punnett square:In incomplete dominance, the heterozygous genotype is represented by a single letter, while in codominance, the heterozygous genotype is represented by a combination of the two letters.
These patterns can affect phenotypic expression in a variety of ways. For example, incomplete dominance can result in a wide range of phenotypes within a population, while codominance can result in distinct and easily identifiable phenotypes.
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap
The Amoeba Sisters video on incomplete dominance and codominance provides a clear and concise explanation of these genetic patterns. The video uses visual aids, such as Punnett squares and diagrams, to illustrate the concepts.
The video also highlights the strengths and weaknesses of these patterns as a learning resource. For example, the video notes that incomplete dominance can be difficult to understand, while codominance is relatively straightforward.
Overall, the Amoeba Sisters video is a valuable resource for students learning about incomplete dominance and codominance.
Top FAQs: Amoeba Sisters Video Recap Incomplete Dominance Codominance Answer Key
What is incomplete dominance?
Incomplete dominance occurs when neither allele in a heterozygous genotype is fully dominant over the other, resulting in an intermediate phenotype.
How does codominance differ from incomplete dominance?
In codominance, both alleles in a heterozygous genotype are expressed equally, resulting in a distinct phenotype that combines the traits of both alleles.